In the evolving landscape of digital privacy and security, 3rd party cookies have become a hot topic. These small pieces of data, stored on a user’s device by websites other than the one they are currently visiting, have been both a boon and a bane for the internet. For developers and tech enthusiasts, understanding the role and impact of 3rd party cookies is crucial. This post will delve into their history, usage by big companies, and the controversies surrounding them.

The Origins of 3rd Party Cookies
Cookies, in general, were introduced by Netscape Communications in 1994 to facilitate online transactions. Initially, cookies were designed to store stateful information, such as shopping cart contents, session identifiers, and user preferences, directly on the user’s device. However, as the internet grew, so did the use of cookies for other purposes.
3rd party cookies emerged as a way for advertisers to track users across different websites. Unlike first-party cookies, which are set by the website the user is visiting, 3rd party cookies are set by external domains, typically advertising networks or analytics platforms. This allowed for more sophisticated tracking and profiling of users, leading to more targeted advertising.
How 3rd Party Cookies Work
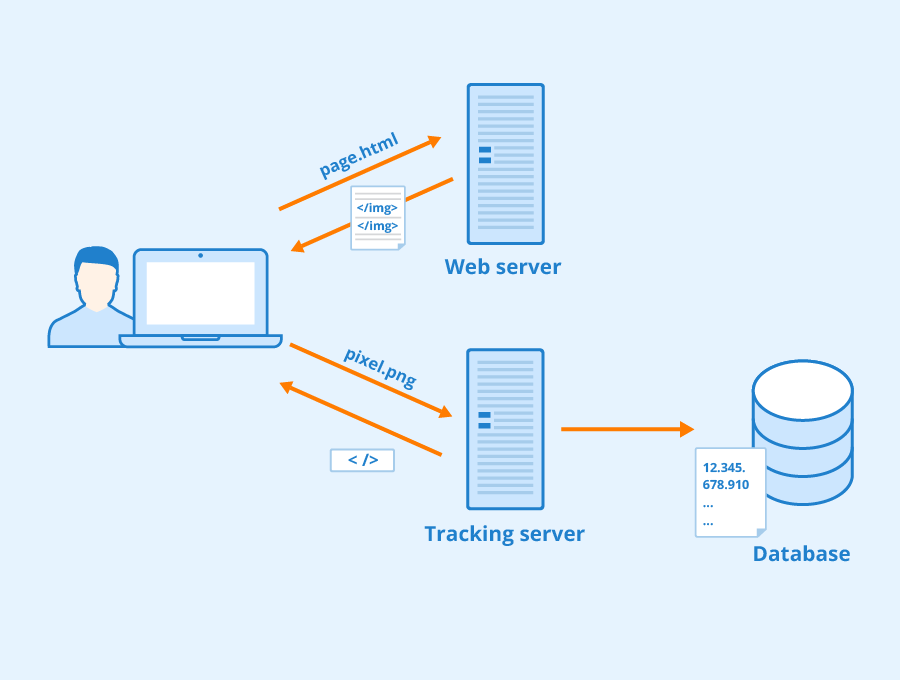
When a user visits a website, the site may include elements such as ads, social media widgets, or analytics scripts that load content from external servers. These external servers can set their own cookies on the user’s browser, which are then accessible whenever the user visits another site that loads content from the same external server.
This mechanism enables advertisers to build detailed profiles of users by tracking their behavior across multiple websites. For instance, if you visit a travel blog and later an airline’s website, both loading ads from the same ad network, that network can infer your interest in travel and serve you targeted ads accordingly.
The Role of Big Companies
Several major companies have leveraged 3rd party cookies to dominate the online advertising space. Google, Facebook, and Amazon are prime examples of entities that have used these cookies extensively to gather data and drive their ad businesses.
Google: As the largest digital ad company, Google has utilized 3rd party cookies through its ad services like Google Ads and DoubleClick. By tracking user behavior across millions of websites, Google can offer highly targeted advertising solutions, significantly boosting the effectiveness and profitability of its ad campaigns.
Facebook: With its social plugins and pixels embedded across various websites, Facebook has been able to track users even when they’re not on the platform. This data collection has allowed Facebook to build comprehensive user profiles, enabling precise ad targeting and substantial revenue generation.
Amazon: Although primarily known as an e-commerce giant, Amazon’s advertising business has grown rapidly. By tracking user activity on its platform and across the web, Amazon can deliver highly personalized ads, contributing to its burgeoning ad revenue.
Controversies and Privacy Concerns
While 3rd party cookies have enabled significant advancements in digital marketing, they have also raised substantial privacy concerns. Users often have little awareness or control over the data being collected about them, leading to growing unease and regulatory scrutiny.
Data Privacy Issues: 3rd party cookies track users without explicit consent, leading to a pervasive sense of being watched. This invasive tracking has sparked numerous debates about digital privacy and the ethical use of user data.
Regulatory Actions: In response to privacy concerns, several regulations have been introduced to curb the misuse of cookies. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) are prime examples of legislation aimed at giving users more control over their data. These regulations require websites to obtain explicit consent before setting cookies and provide users with the option to opt-out of tracking.
Browser Changes: Major web browsers have taken steps to phase out 3rd party cookies. Safari and Firefox have implemented measures to block 3rd party cookies by default, and Google Chrome has announced plans to do the same by 2023. These changes are aimed at enhancing user privacy and addressing the misuse of cookies for tracking purposes.
The Future of Advertising and User Tracking
As the industry moves away from 3rd party cookies, alternative methods of tracking and targeting users are emerging. These methods aim to balance effective advertising with user privacy.
First-Party Data: Companies are increasingly focusing on collecting first-party data, which is obtained directly from their own websites or apps. This data is considered more reliable and privacy-compliant, as it involves direct interactions with users who have willingly provided their information.
Contextual Advertising: Rather than relying on user profiles, contextual advertising targets ads based on the content of the webpage being viewed. This method does not require tracking users across the web and aligns better with privacy regulations.
Privacy Sandbox: Google’s Privacy Sandbox is an initiative aimed at developing new standards for online advertising that protect user privacy. It proposes technologies that limit data collection while still allowing for relevant ad targeting. One such proposal is the Federated Learning of Cohorts (FLoC), which groups users with similar interests together, reducing the need for individual tracking.
User-Centric Approaches: Empowering users with greater control over their data is becoming a priority. Tools like browser extensions and privacy settings allow users to manage their cookie preferences and block unwanted tracking.
Conclusion
3rd party cookies have played a pivotal role in shaping the digital advertising landscape, enabling sophisticated tracking and targeting mechanisms. However, their invasive nature and associated privacy concerns have led to significant backlash and regulatory action. As the industry transitions away from 3rd party cookies, new methods and technologies are emerging to ensure effective advertising while respecting user privacy.
For developers and tech enthusiasts, understanding the evolution and impact of 3rd party cookies is essential. By staying informed about emerging trends and technologies, they can navigate the changing landscape of digital privacy and contribute to a more secure and transparent online environment.






